Data visualization plays a role in transforming the way we interpret and convey information effectively. Why is it so important in today's context? How does it actually work? This guide is here to give you some answers and practical insights.
Data visualization combines design, business goals, and data analysis to create a tool that helps people make better decisions and improve their work. By translating data into representations, we gain the ability to uncover hidden patterns, trends and insights within the data, allowing us to unravel complexities and present information in a clear format for others.
In comparison to methods of data analysis, visual representations significantly improve our capacity to understand and communicate insights. Processing information through means is not only faster but also more comprehensible.
Bring your data to life with Justinmind's free prototyping tool.

This guide explores the principles of data visualization alongside industry best practices, diverse visual formats, practical examples from real world scenarios as well as leading software solutions.
Let’s take a closer look at the fundamentals of data visualization and see how we can transform data into compelling visuals.
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. Data visualization tools use visual components, making it easier for individuals to identify trends, outliers, and patterns within seconds. The goal is to allow anybody to take easily digestible and action-oriented insights from data.
These visual elements are extremely useful for simplifying complex data making it accessible to a larger audience. For example, a simple bar chart may compare different categories, but a line graph can show trends over time. Using a wireframe tool early in the design process can help structure these visual elements effectively before finalizing them.
There are several types of graphical data representations, each suited to different kinds of data and analytical needs:
- Bar charts: Ideal for comparing quantities across different categories.
- Line charts: Perfect for showing trends over time.
- Pie charts: Useful for displaying proportions within a whole.
- Scatter plots: Great for revealing relationships between two variables.
- Heat maps: Effective for showing data intensity across a geographical area or a matrix.
- Tree maps: Good for displaying hierarchical data.
Incorporating a charts UI kit can streamline the process of creating these visualizations, ensuring consistency and quality in design.
Data visualization is changing how we understand information. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js let users explore their data directly, making changes and seeing the results in real-time. This interactive approach leads to valuable discoveries and a deeper understanding of the data.
Just think about how handy it would be to always have an interactive dashboard design available. You may quickly and simply filter your sales data according to particular products, time periods, or regions with a few clicks. This custom view not only saves you time, but it also reveals certain details that suit your particular requirements and preferences. You may find hidden patterns and make better decisions based on what your data actually shows by looking at it from various perspectives.
As data visualization turns complex information into simple pictures, it makes understanding easier. For example, a colorful bar chart can quickly highlight the best-performing products, making the data more engaging and easier to understand.
Data visualization simplifies complex information. Graphs, charts, and maps help people quickly understand large amounts of data. For example, a bar chart showing sales figures makes it easy to compare products at a glance, leading to quicker and more accurate insights.
Visualizing data also reveals the story behind the numbers, making it easier to spot trends and patterns, leading to smarter decisions. Tools like Tableau and Power BI enable decision-makers to explore data interactively, diving into specifics to uncover insights. This leads to more informed and timely decisions, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced environment.
Showing data visually is more effective than plain numbers. For example, a pie chart can quickly show the market share of different companies, clearly indicating the leader. This method is especially helpful in presentations and reports, where clear communication is essential for gaining support and driving action.
Visuals can uncover trends and patterns hidden in plain numbers. Dot graphs reveal relationships between two data sets, while line graphs show changes over time. These tools help analysts and decision-makers understand the data better and make smarter choices.
What makes a good data visualization? It’s the ability to capture attention. Have you ever found yourself drawn to an interactive visual that lets you dive into the details? These kinds of visuals make information clearer and more convincing. That’s why they’re so important because they can can boost customer understanding and lead to more sales.
If you struggle with large datasets, visualizations can help by turning complicated information into something simple and manageable. For example, have you ever seen a tree map? It breaks down hierarchical data into clear sections, making relationships easy to see at a glance. This way, what once seemed overwhelming becomes straightforward and understandable.
Modern data tools act like live TV for your business. Dashboards combine info from various sources, showing real-time updates. This is great for monitoring important metrics and reacting quickly to market changes or business needs.
Last but not least, interactive visualizations let users explore data on their own. They can filter information, zoom in on details, and view different perspectives. This hands-on approach often reveals new insights that might be missed in regular reports, making the data even more valuable.
Bring your data to life with Justinmind's free prototyping tool.

As we have seen, the importance of data visualization lies in its ability to transform complex data into clear, actionable insights. To achieve this effectively, let’s delve into the key principles of effective data visualization.
Know your audience: Think about who will be viewing your data. Tailor your visualizations to match their needs and knowledge levels. This way, everyone can easily understand the information.

Consider this: a team of experts might want to delve into the nitty-gritty details, while executives might prefer a high-level overview highlighting key insights. Tailoring your visualizations to meet these specific needs ensures your message resonates with the right people.
Tell a story: If you use your visuals to guide viewers through the data, you’ll be able to highlight key discoveries and conclusions. This way, it will be more engaging and easy to follow, like telling a story.
Choose the right chart: As mentioned earlier in the types of data visualization, picking the best type of chart for your data is crucial. Whether it’s bar charts for comparisons or line charts for trends, using the right visual will make a difference.
Keep it simple: Less is more. Focus on the most important data points and avoid clutter. Clean and simple visuals are easier to understand.
Use colors wisely: Color can make your data pop, but use it thoughtfully. Highlight key information, distinguish between categories, and keep your color scheme consistent.
Provide context: Add benchmarks, annotations, and clear titles to paint a complete picture for your audience. Giving context makes your data more meaningful and much easier to understand.
Ensure accuracy: Lastly, double-check your data and use correct scales. Avoid anything that could mislead your audience. Accurate visuals build trust and support informed decisions.
Avoid overwhelming your audience with too much data. Overcrowded visuals can be hard to interpret and obscure the main message. Focus on the most relevant points and use visual hierarchy to highlight key information.
Make sure the scales on your graphs and charts are correct. Messing with scales to make things look bigger or smaller than they really are can confuse people and lead them to wrong conclusions. Always use scales that show the information truthfully.
Before you even think about creating visuals, make sure your data is clean and well-prepared. Raw data often has errors, missing pieces, and inconsistencies that can throw off your results. Think of it as tidying up before guests arrive – you want everything in order. Proper preparation means cleaning, formatting, and verifying your data so it’s accurate and reliable.
Once your data is ready, the next step is choosing the right visuals. It’s not just about picking any chart or color scheme. The wrong choices can make your information confusing or even misleading. Imagine trying to read a cluttered map – it’s frustrating and unhelpful. Use visuals that clearly and accurately convey your data, making it easy for your audience to grasp the key points.
Finally, don’t forget the power of interactivity. Static visuals can be informative, but interactive ones take it to the next level. They allow users to explore the data, filter information, and zoom in on details they find interesting. It’s like turning a static picture into a dynamic experience. This interactive approach not only makes the data more engaging but also leads to deeper insights.
Now that you know how to make great data visualizations, let’s dive into understanding data itself and picking the right tools to show it off. We’ll cover the different types of data, where to find it, and how to get it ready for visualization. We’ll also discuss different charts and how to choose the best one for your data based on your goals.
Data comes in two main types.
Quantitative data: This is all about quantities, the things you can count or measure. Think sales numbers, temperatures, or how many points someone scored in a game. This kind of data often shows up in charts with exact numbers, like bar charts, line charts, and scatter plots.
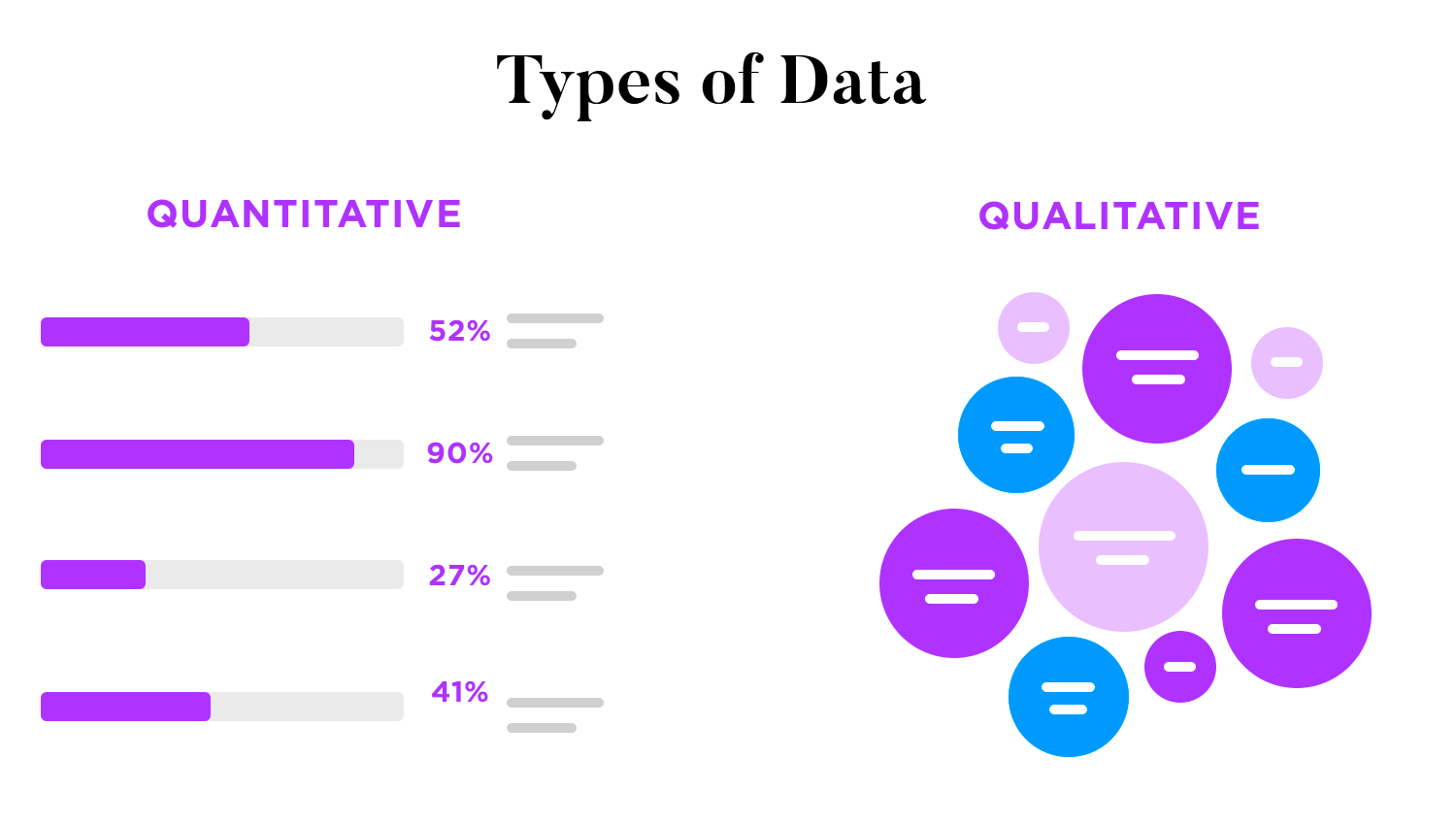
Qualitative data: This is about qualities, the words that describe things like customer reviews, interview quotes, or product descriptions. This data is often visualized in word clouds or bar charts that group words into categories.
Data is everywhere, and knowing where to look is key to making effective data visualization.
Internal sources: This is data your own company or team has gathered. Think sales reports, notes about how your employees are doing, and any surveys you’ve run. This data is usually right on target for what you need.
External sources: In this case, you get the information from other places, like public databases, research reports, or other companies. Imagine things like market studies, social media trends, or government stats. This kind of data helps you see how your own numbers compare and gives you a wider view.
Before visualizing data, it’s essential to prepare it properly. This means cleaning it up and organizing it to make sure it’s accurate and you can trust it.

Data cleaning: This step is like tidying up. You’re finding and fixing errors in your data, like missing info, doubles, or things that don’t make sense. Tools like Excel, Python, or special software can help you do this faster.
Data transformation: Once your data is clean, you might need to change it into a format that’s easier to work with. This could mean making all the numbers similar, making new calculations from your data, or changing the way the data is written.
Data validation: The last step is like a double-check. You’re making sure the data is a true reflection of reality. This means finding any unusual numbers, comparing your data to known standards, and making sure everything in the data set is consistent.
When deciding how to effectively show your data, it’s important to first understand your numbers. Are you dealing with quantities or qualities? What story are you trying to tell with them? For example, if your data is time-related, a line chart might be best, while a scatter plot could showcase the relationship between two sets of values.
Next, think about your goal. What message do you want your audience to take away from this visualization? If you’re showing parts of a whole, a pie chart is a good choice, but if you’re comparing groups, a bar chart might be more effective.
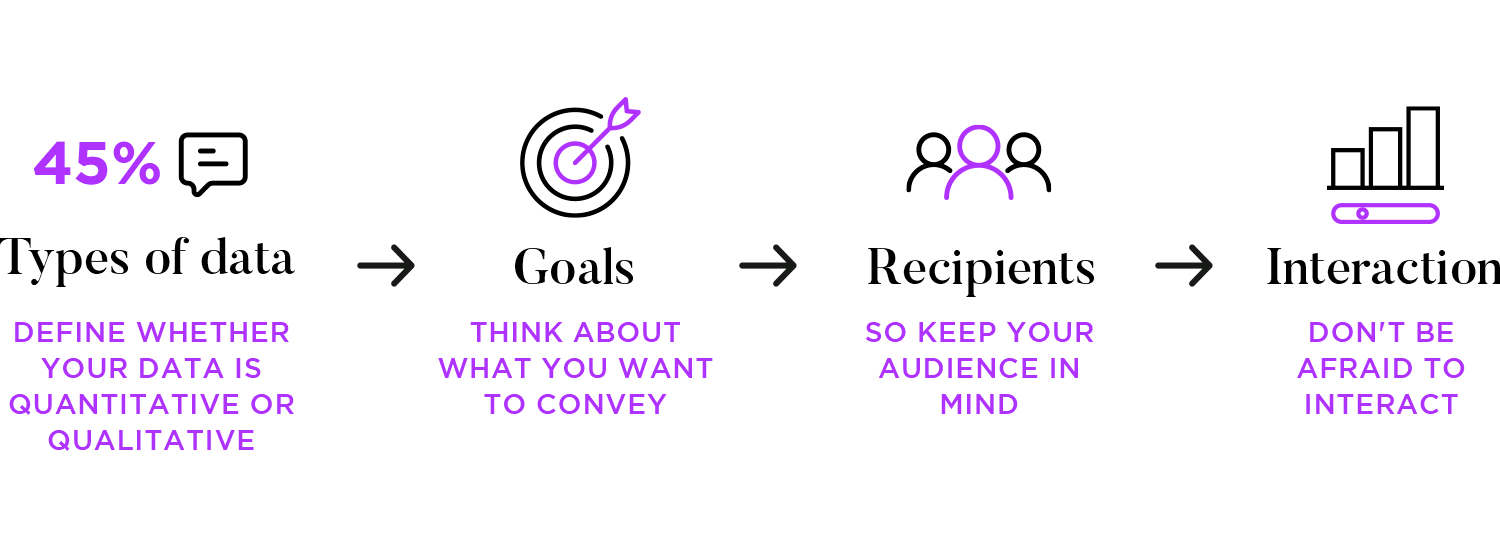
Also, keep your audience in mind. Technical people can handle more complex visualizations, while executives might prefer something simpler. No matter who your audience is, strive for clarity and make sure every element on the chart has a purpose.
Finally, if you’re dealing with larger datasets, don’t be afraid to get interactive! Tools like Tableau or Power BI can allow users to explore your data more deeply. By following these guidelines, you’ll be well on your way to creating data visualizations that are both informative and engaging.
We’ve talked about how powerful data visualization can be in turning complex data into clear and engaging stories. Now, let’s see it in action! Here are 20 fantastic examples of data visualizations from different areas. These examples show various ways to visualize data and use different tools, giving you practical ideas for your own data presentations.
This example of data visualization uses a colorful pie chart brimming with images of food to visually represent different food categories and their consumption percentages. Each slice clearly shows the percentage it represents, while additional information is provided in infographics alongside the chart for a more detailed look.
The bright colors and realistic images make the chart eye-catching, helping people not only understand the information better but also remember it longer. This type of visual is perfect for educational tools and marketing materials where grabbing attention is key.
Here’s an engaging example of data visualization using a network graph to showcase connections and interactions. Circles of various sizes and colors represent different data points, connected by lines to illustrate relationships.
This interactive design allows users to explore relationships and dive into specifics with ease. Ideal for business analytics, this visualization makes complex data simple and captivating.
This striking data visualization example from the AMS Data Visualization System uses bold infographic panels to present various data points clearly and engagingly. Each panel features large, easy-to-read text and visuals such as percentages, line graphs, and circular charts to convey information quickly.
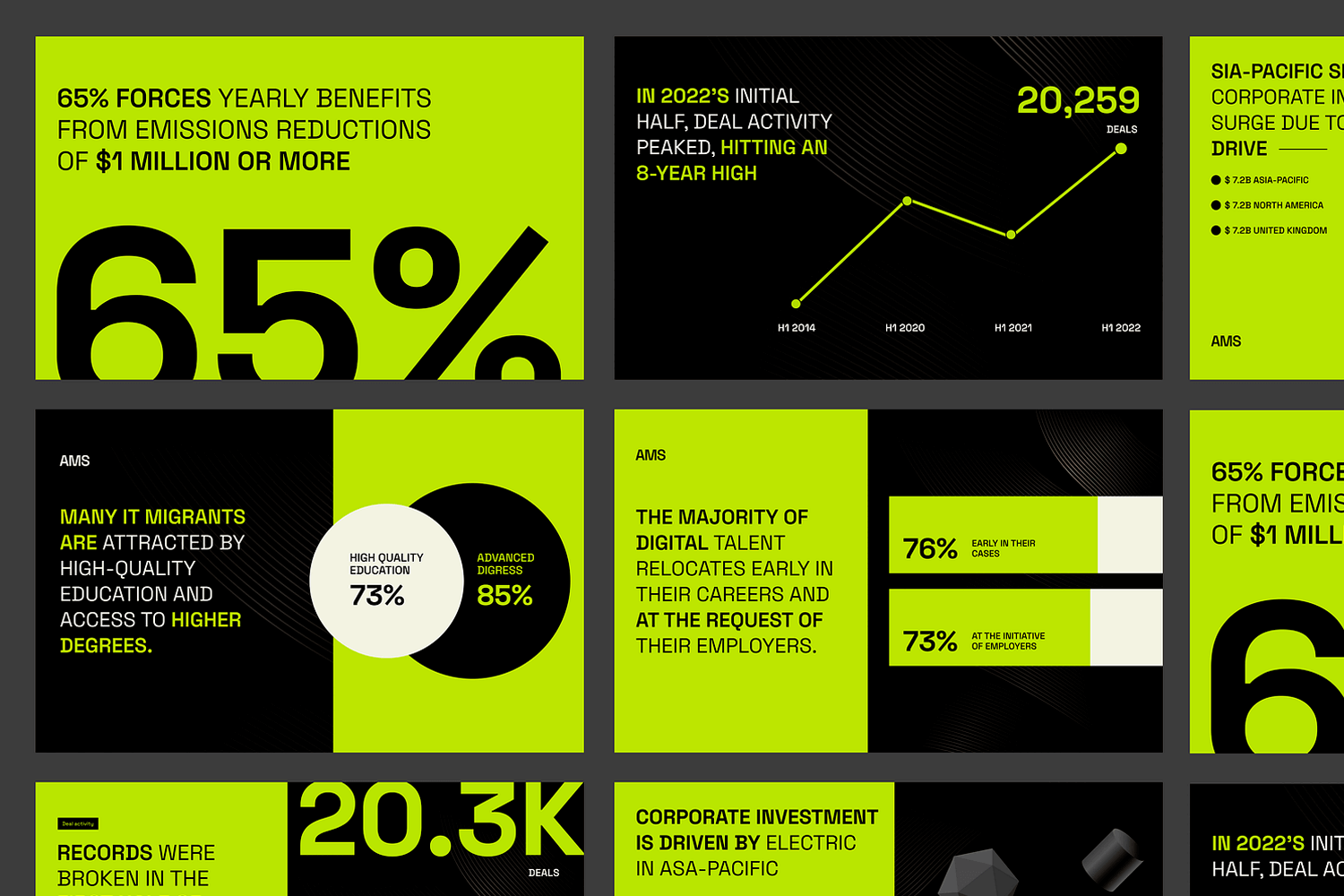
The bright colors and strong contrasts help the data pop, making sure important insights are easy to see right away. This design is ideal for company reports, presentations, and dashboards, where it’s essential to make complex data simple and eye-catching.
We chose this example of data visualization for its clear and engaging design. The top section features a colorful circular gauge displaying the event value score, with segments for answer quality, question efficiency, and answer efficiency.
A bubble chart shows changes in these metrics over the year. The guest behavior section uses flow charts and pie charts to illustrate attendee actions like browsing, searching, and submitting questions.
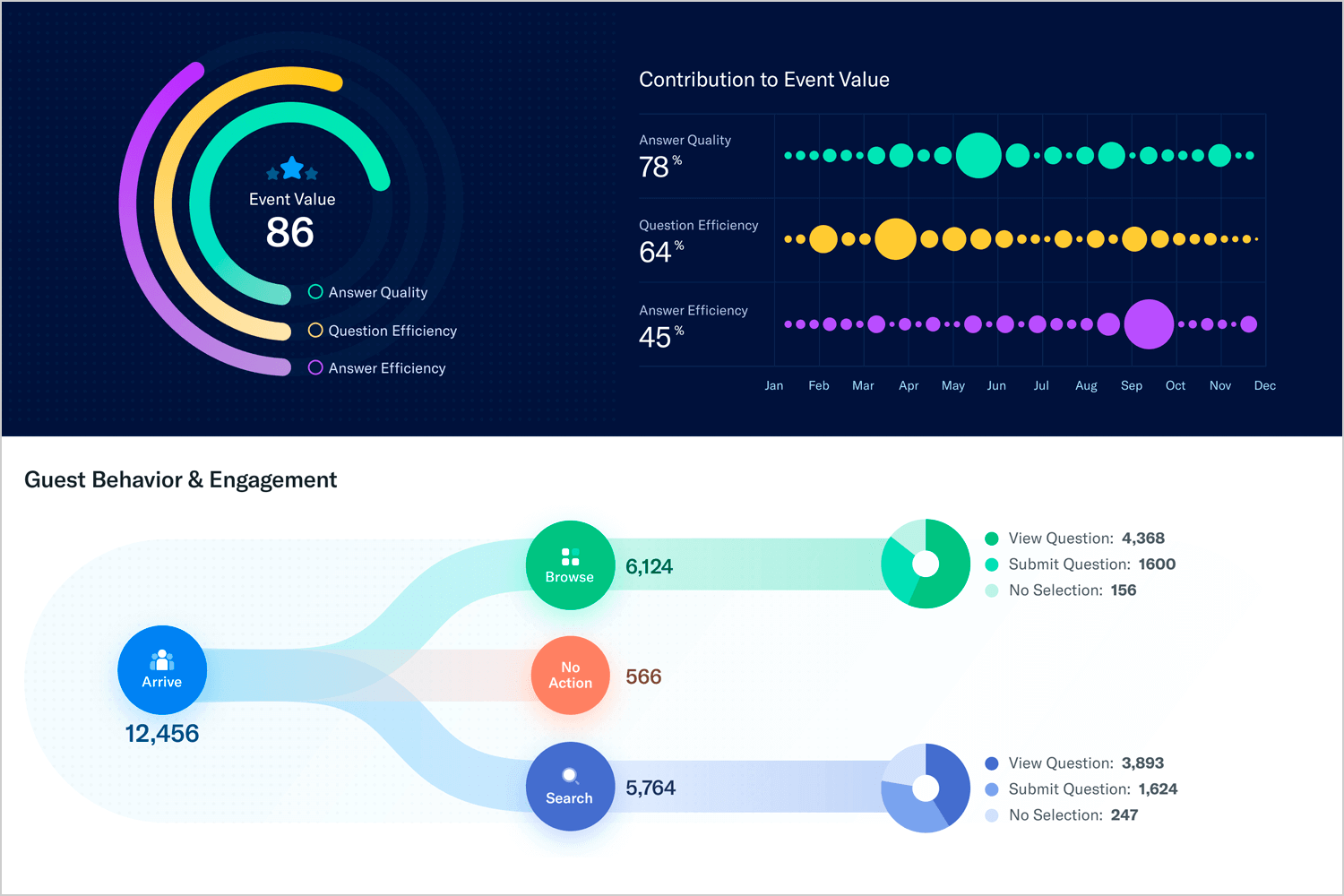
This user-friendly design makes complex data easy to understand, ideal for event management and performance analysis.
This is a great data visualization example for its simple and effective presentation of statistics. The left side of the design displays key percentages like 85% for feedback accuracy and 30% for employee satisfaction improvement, using horizontal bars to illustrate the data.
On the right, a photo of a team working together adds a human touch. This layout makes the data easy to understand and visually appealing.
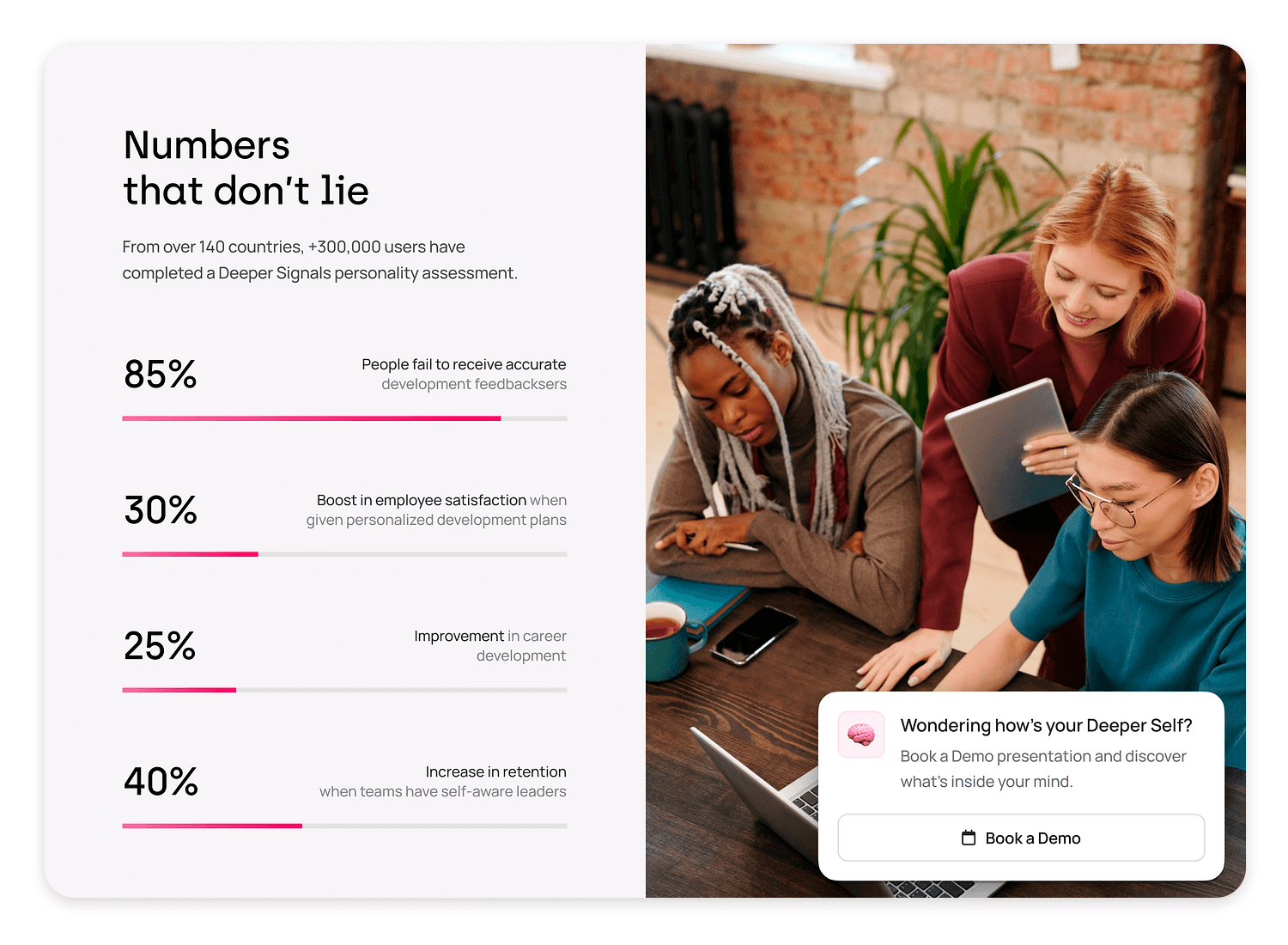
Ideal for reports and presentations, this design highlights important numbers clearly and engagingly.
This example of data visualization is a fun and creative presentation of the 100 biggest LEGO sets. The design features a colorful tower made of LEGO bricks, each representing different sets. Below, a circular chart provides detailed information about each set, including public ratings, pricing, and build time.
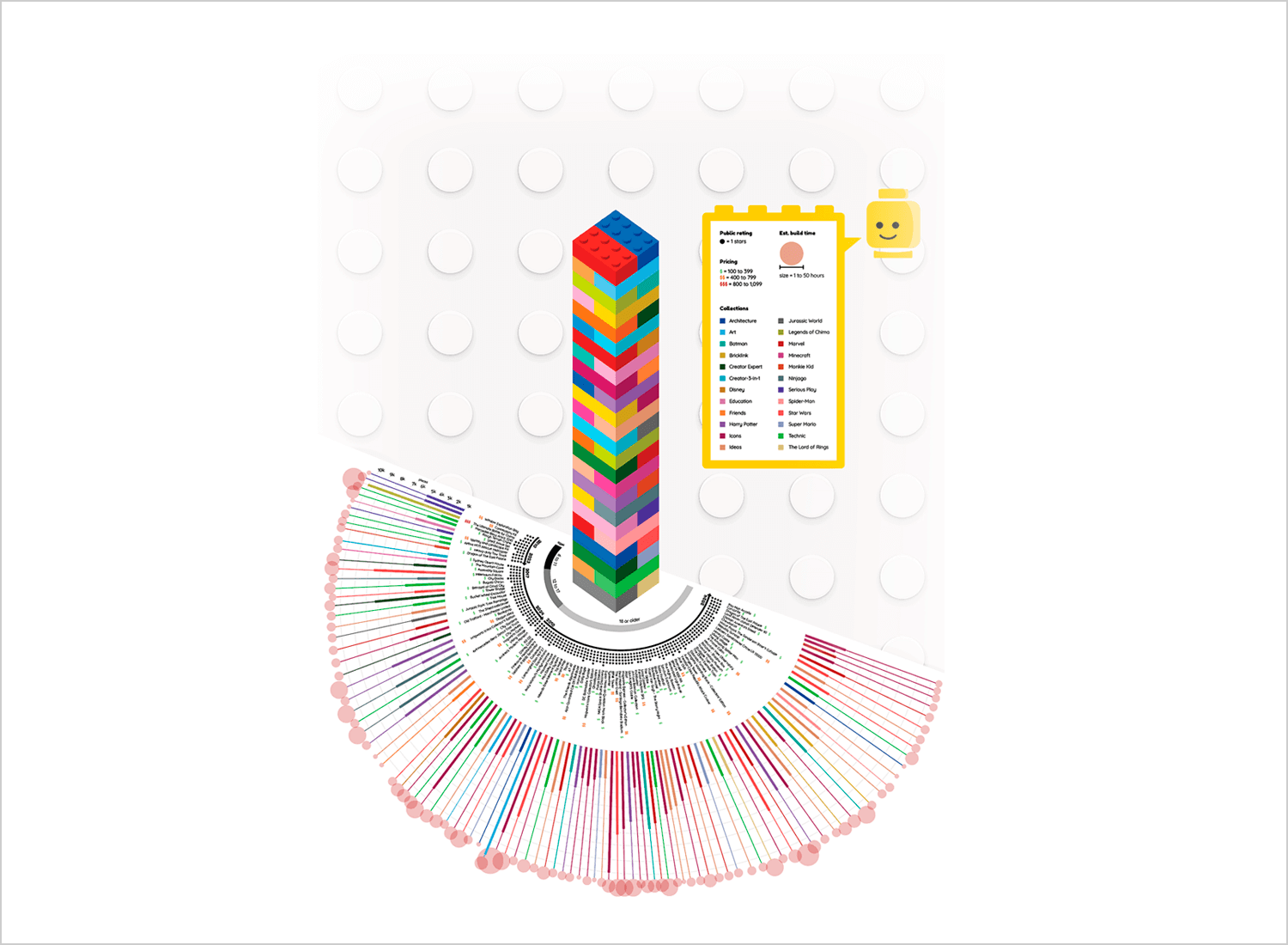
This engaging and visually appealing layout makes the data easy to understand and enjoyable to explore. Perfect for presentations and reports, this design highlights data in a playful yet informative way.
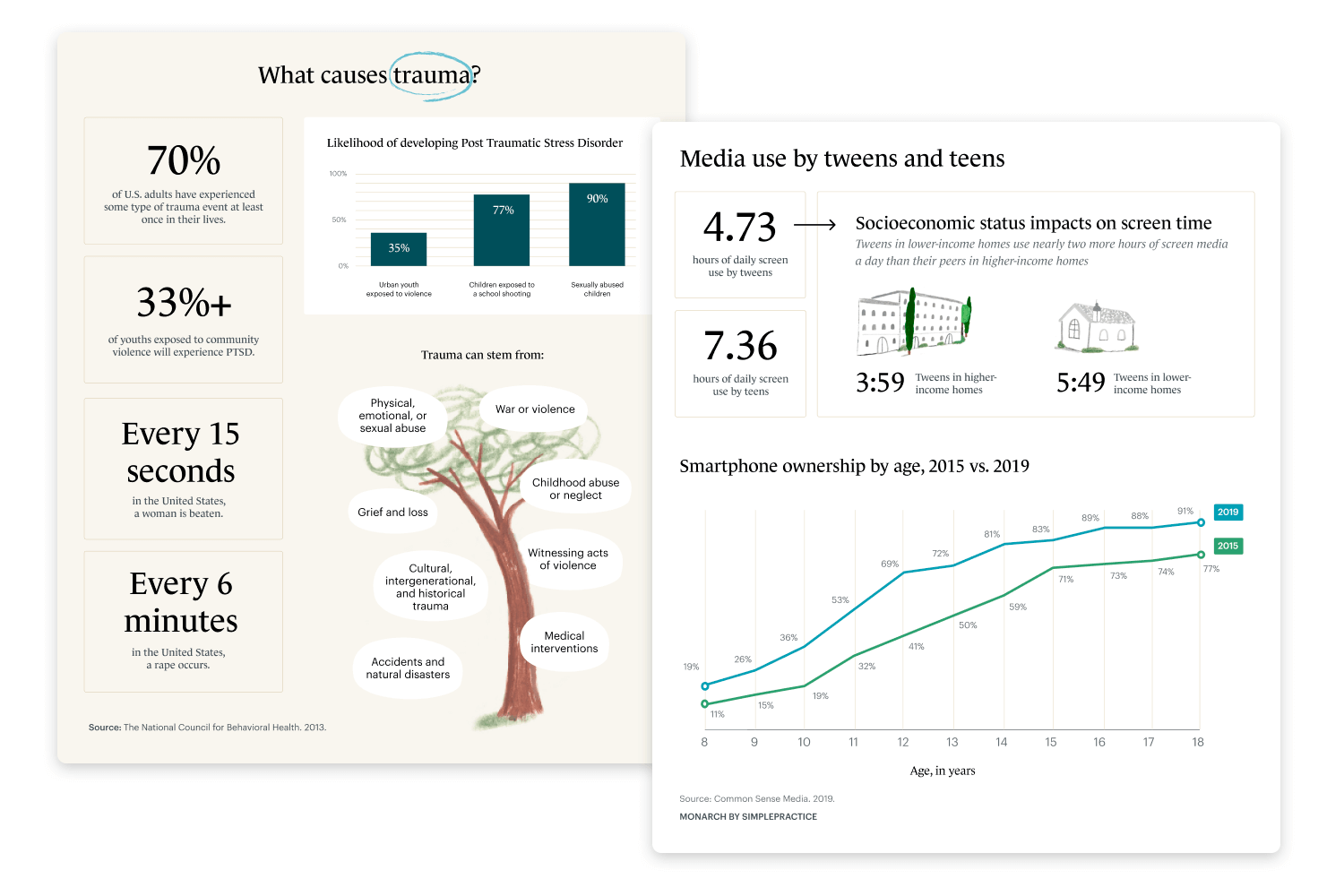
Here’s a compelling example of data visualization that presents important information on trauma and media use among tweens and teens. On the left, it shows statistics about trauma, including the likelihood of PTSD and various causes of trauma, illustrated with a tree diagram.
On the right, it displays media usage, showing screen time differences based on socioeconomic status and a line chart of smartphone ownership over time. This design makes complex data easy to understand and visually appealing, perfect for educational and healthcare use.
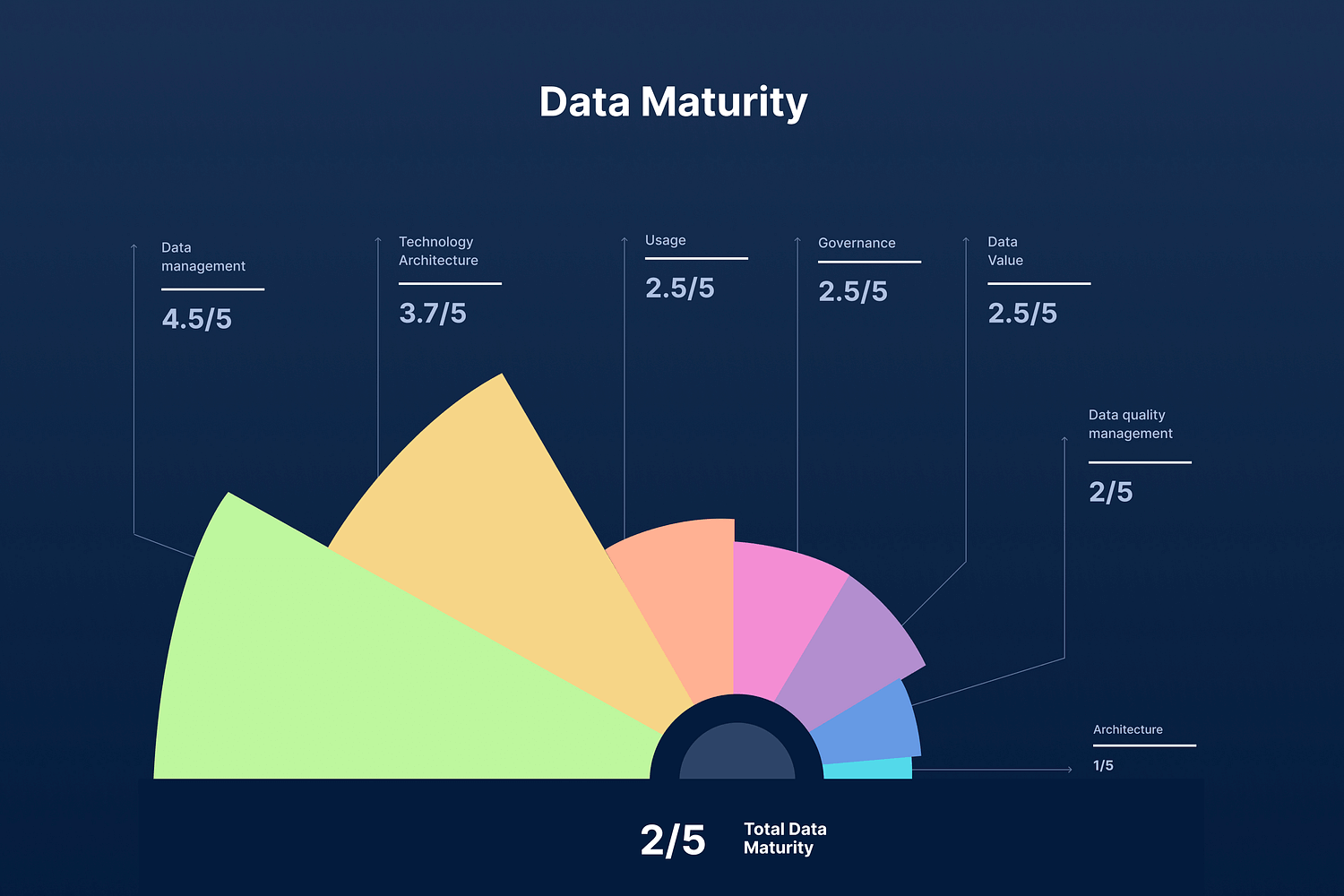
We love this example of data visualization for its engaging and colorful design that explains data maturity. Each section of the chart, in vibrant colors, represents different areas like data management, technology, usage, and governance, all scored out of 5.
This visual makes it easy to spot strengths and areas for improvement at a glance. The overall data maturity score is clearly displayed at the bottom. This eye-catching design helps quickly make sense of complex information, perfect for business analysis.
Take a look at this example of data visualization that features a dynamic dashboard with various data widgets. Each widget provides insights into different metrics like page views, goal completions, active users, and income. The combination of charts, gauges, and lists makes it easy to grasp important information quickly.
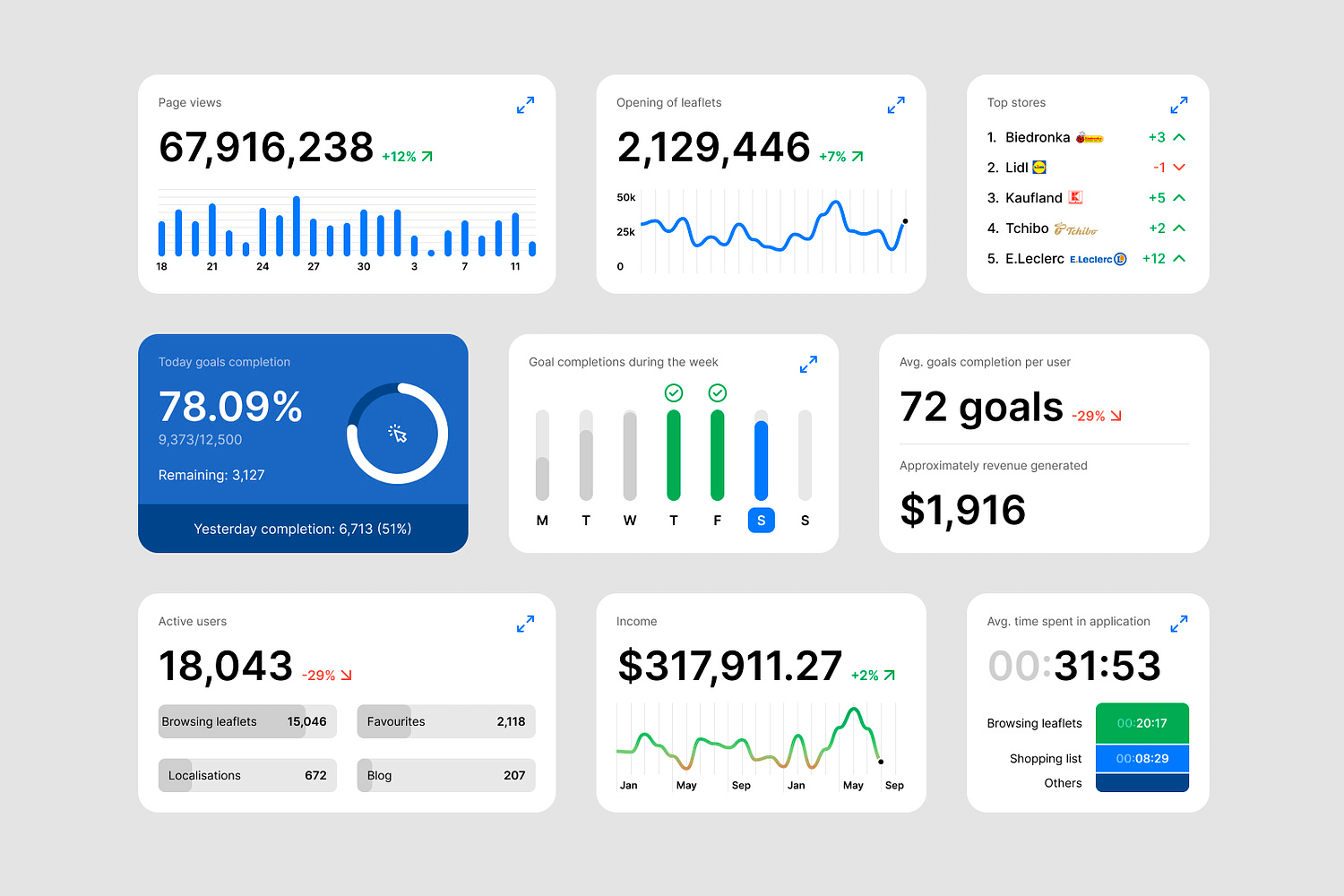
With its clean and modern design, this type of data visualization is perfect for tracking business performance and supporting data-driven decision-making.
Bring your data to life with Justinmind's free prototyping tool.

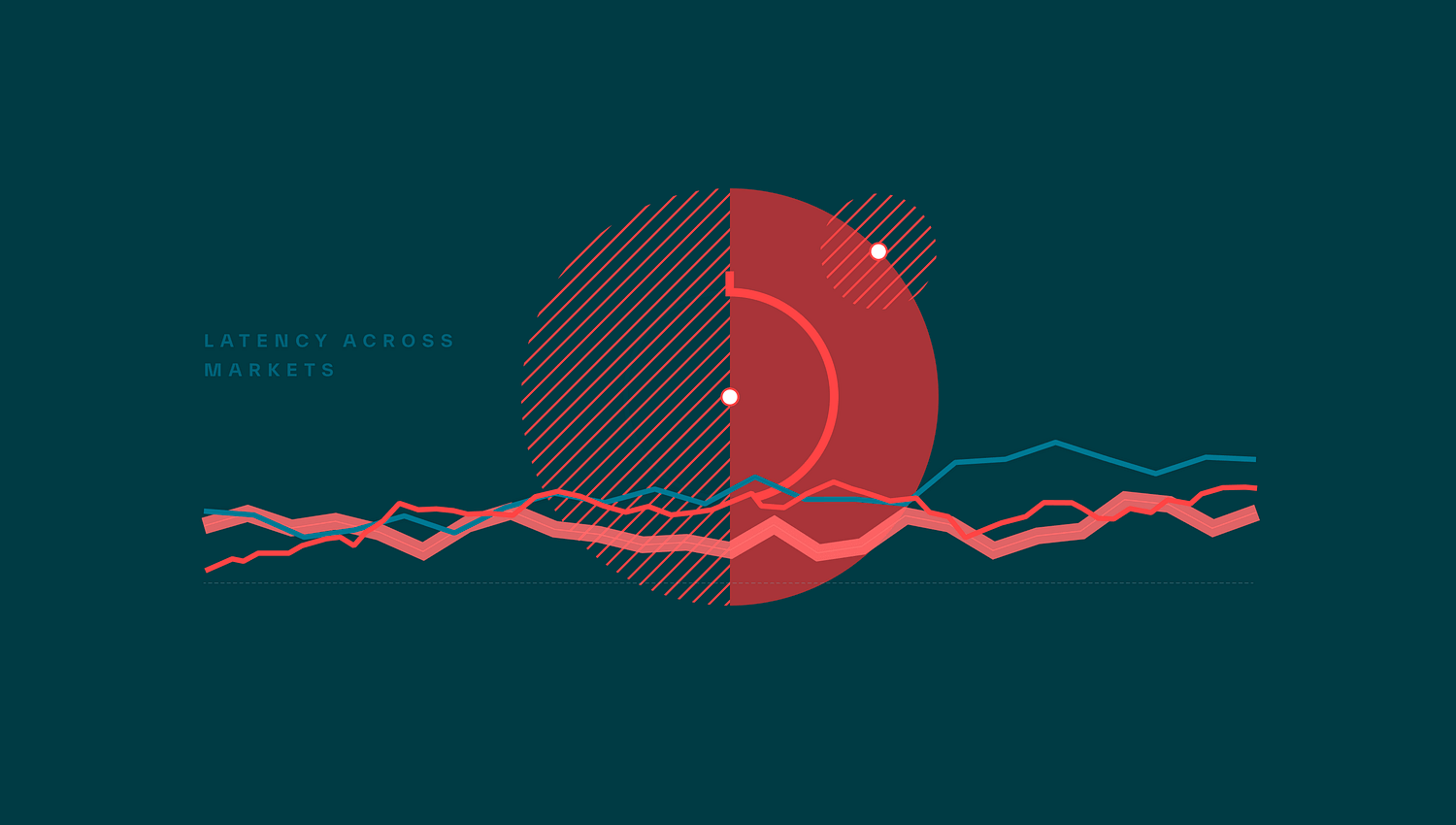
Check out this cool example of data visualization showing market latency. It uses red and blue lines to track changes over time, with circles adding extra details. The simple design and strong colors make the data easy to read and understand, highlighting important patterns.
This clean and modern look is perfect for presenting market performance data in an engaging way.
This engaging data visualization example is designed for mobile devices. Each screen features interactive charts and graphs, including bar charts, line graphs, and circular indicators. The vibrant and dynamic visuals make it easy to track changes and understand key metrics quickly.
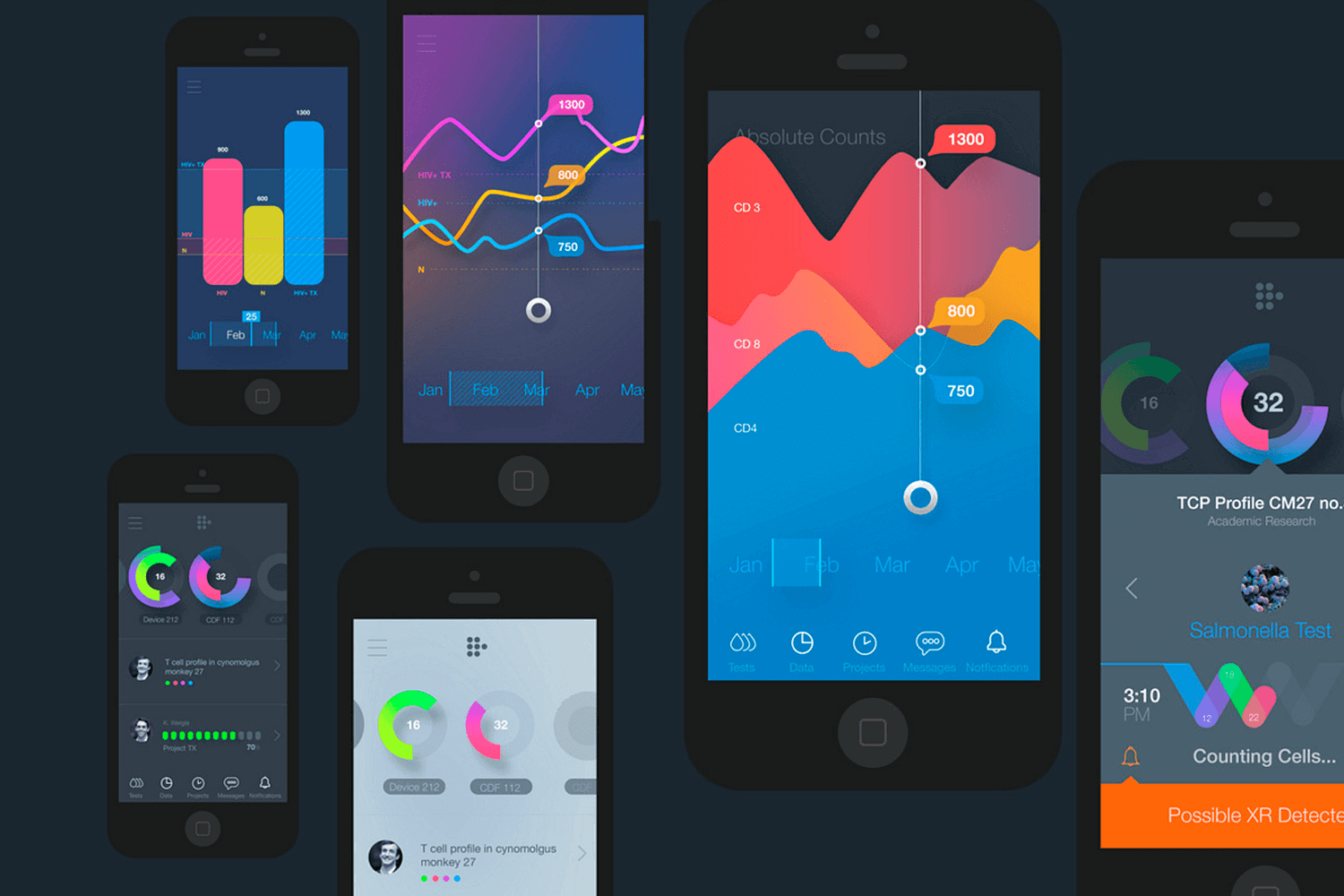
This mobile-friendly design is perfect for real-time data monitoring, providing a clear and engaging way to access complex information on the go.
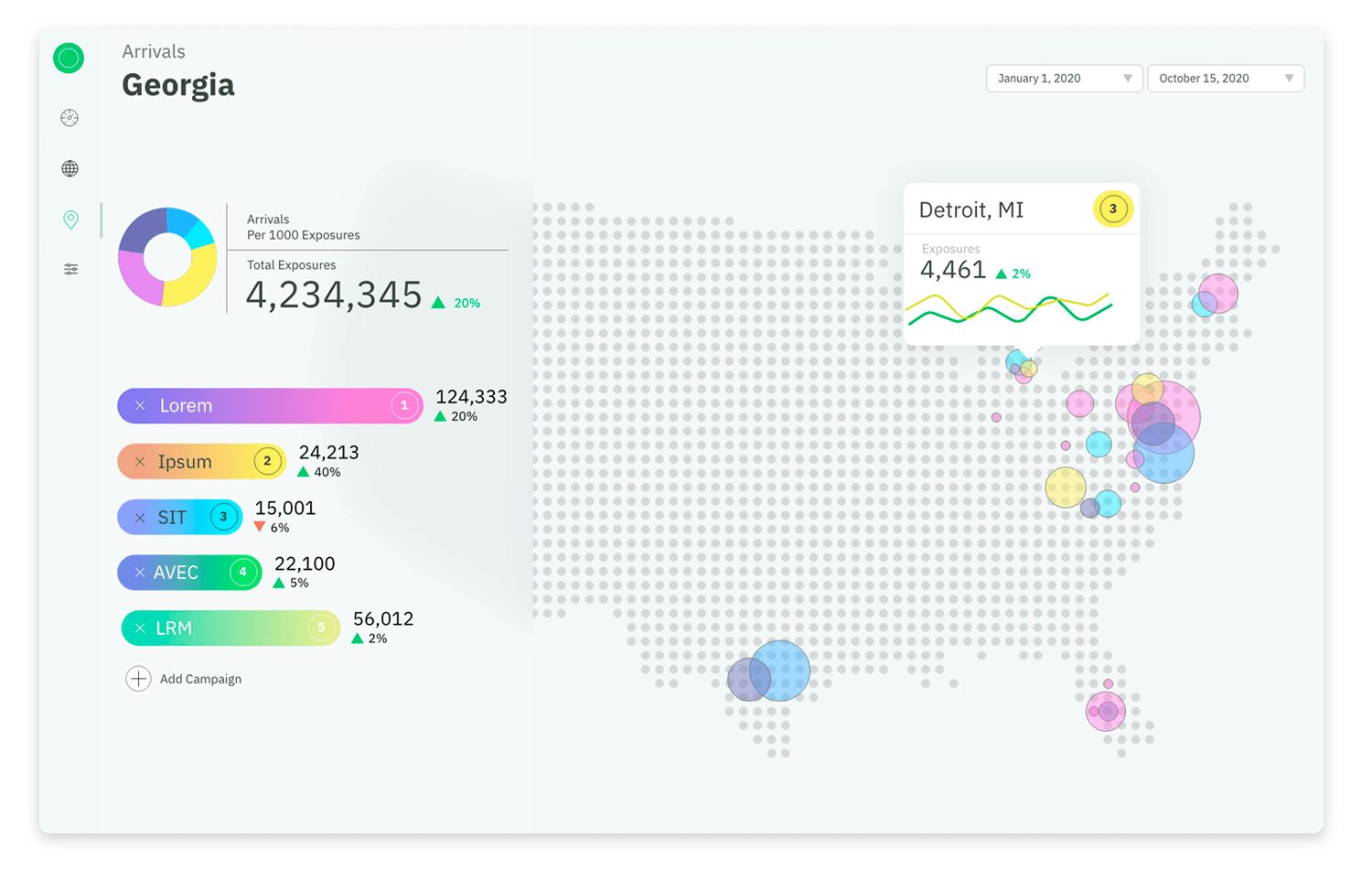
Moving from our last example, this engaging visualization uses an interactive map to show arrival data in Georgia. Alongside the map, there’s a pie chart and a colorful list of campaigns with their statistics.
Hovering over places like Detroit, MI, reveals detailed information, such as exposure numbers and trends. The bright colors and clear design make complex data easy to understand and visually interesting. This type of visualization is great for tracking regional data and performance metrics.
Even complex data can be made clear and engaging with the right design. This crime rate comparison visualization uses a circular chart to show crime trends in different neighborhoods. Each segment represents a neighborhood, with colors indicating recent changes in crime rates.
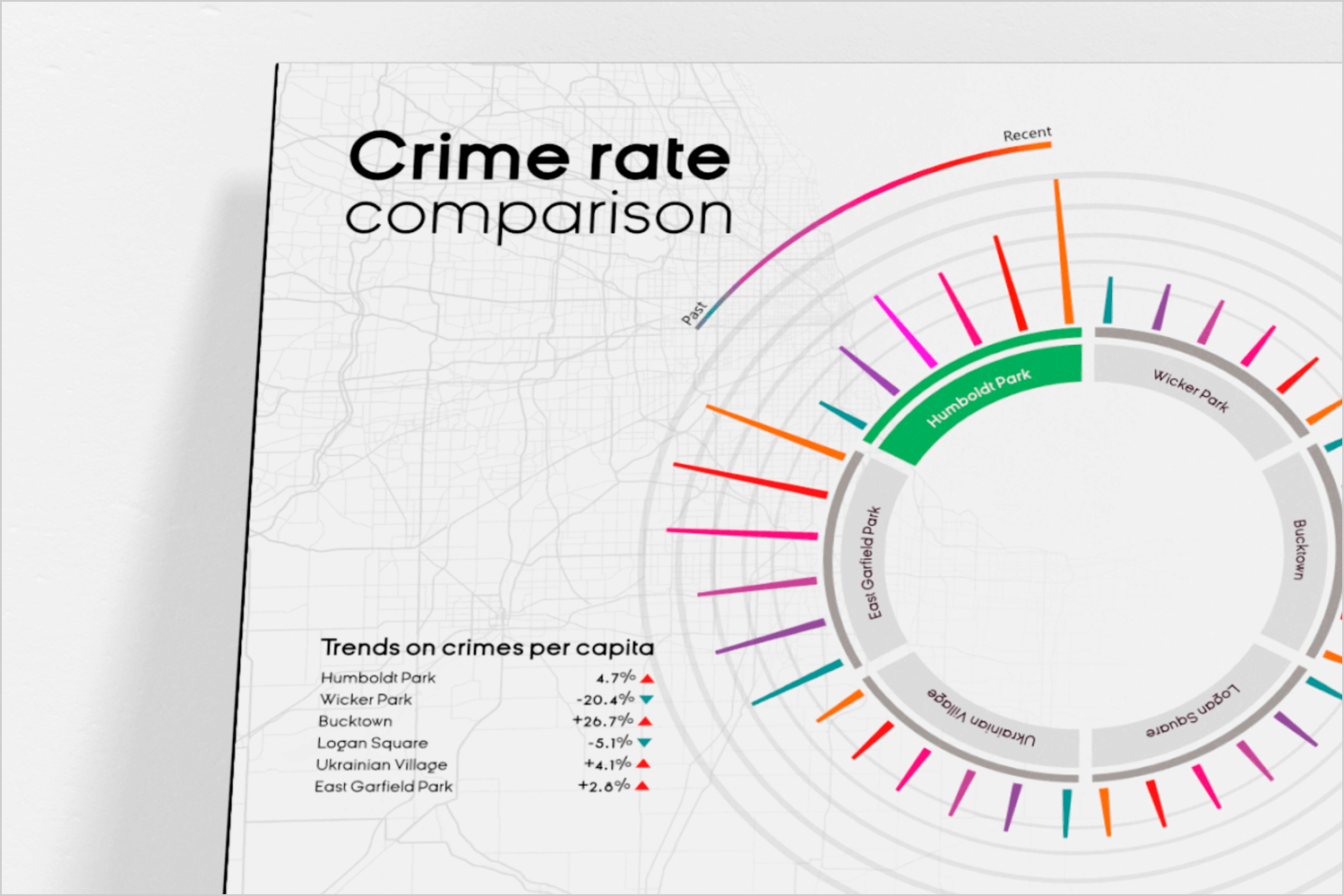
The chart makes it easy to compare crime trends across various areas, with clear labels and color codes to highlight increases and decreases in crime. This type of visualization is perfect for presenting detailed data in a way that is both informative and visually appealing.
Diving into global trends, this example uses a mix of pie charts, line graphs, and area charts to present various data points. The visualizations cover themes like COVID-19, energy use, and international relations.
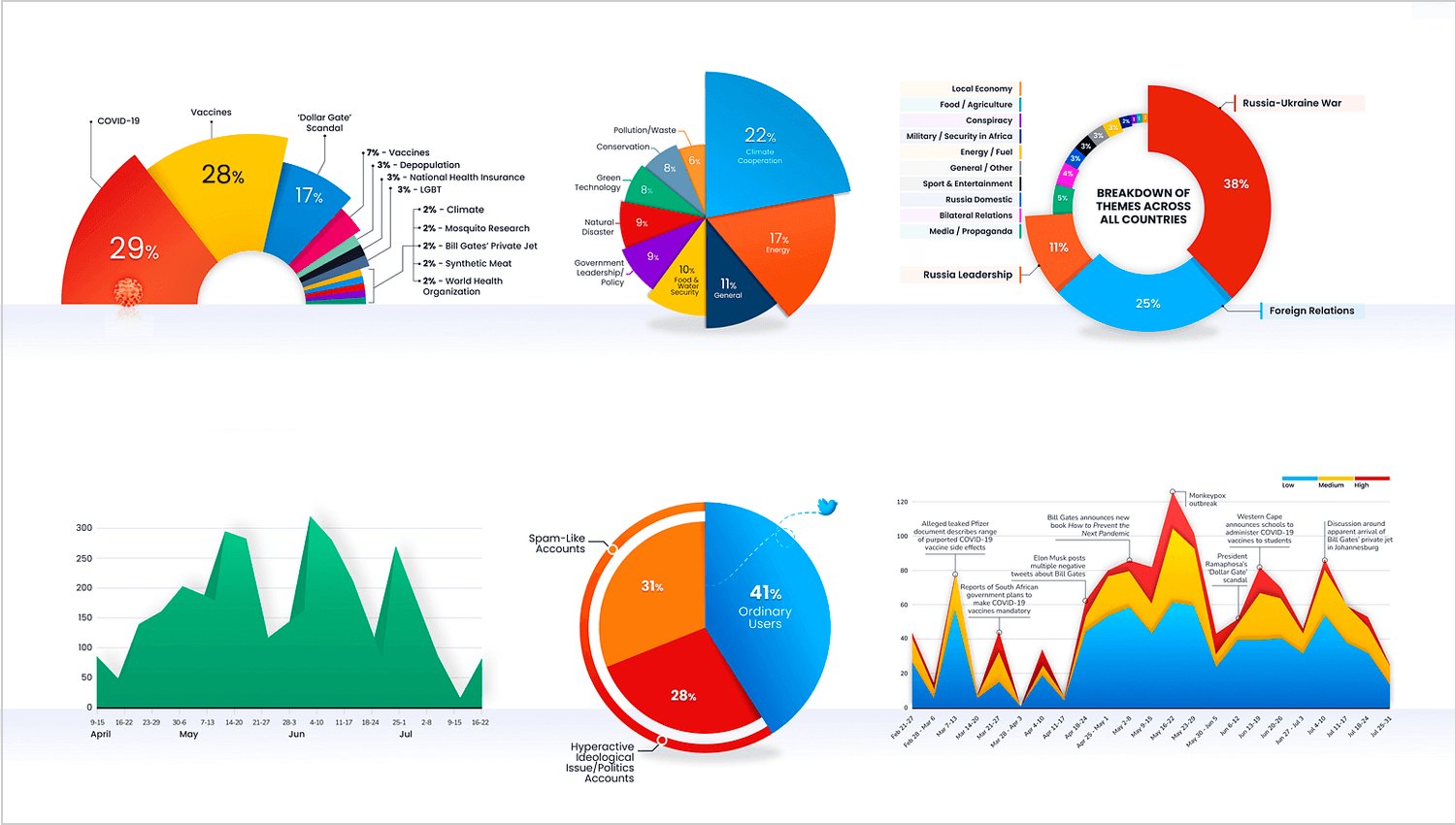
Each pie chart breaks down different themes by percentage, while the line and area charts show trends over time, making it easy to see how these issues evolve. The colorful and well-organized design helps viewers quickly understand complex information.
Here’s an easy-to-understand example of global data comparison. Each column represents a different country, showing positive, neutral, and negative data outcomes in clear bubbles. Below, a circular chart adds more details, making the information comprehensive and easy to grasp.
The pastel colors and clean design help viewers quickly compare and understand complex data. This type of data visualization is perfect for comparing international trends and presenting global data in a straightforward way.
Here’s a versatile example of data visualization components. The main graphic shows a central data point with flows to various subpoints, making it easy to track connections. Below, different types of charts are displayed, including pie charts, line graphs, and a unique squid chart.
The use of vibrant colors and clean design helps make complex data easy to understand. Perfect for presenting diverse data in a clear and engaging way.
This is a futuristic example of data visualization that uses sleek graphics and glowing neon colors to create an engaging and modern look. It features a combination of circular graphs, bar charts, and line graphs, all with a high-tech 3D effect.
The layout is clean and stylish, making complex data easy to read and understand. This type of visualization can transform dull data into something visually striking and captivating, perfect for grabbing attention and making data analysis more interesting.
This data visualization technique shows energy usage in a sleek, modern design. The dark background with green and white details looks clean and professional. The dashboard uses bar charts, line graphs, and numbers to display daily and weekly energy use.
The clear labels and simple graphics make it easy to understand the data quickly. This design helps users track their energy consumption and make informed decisions.
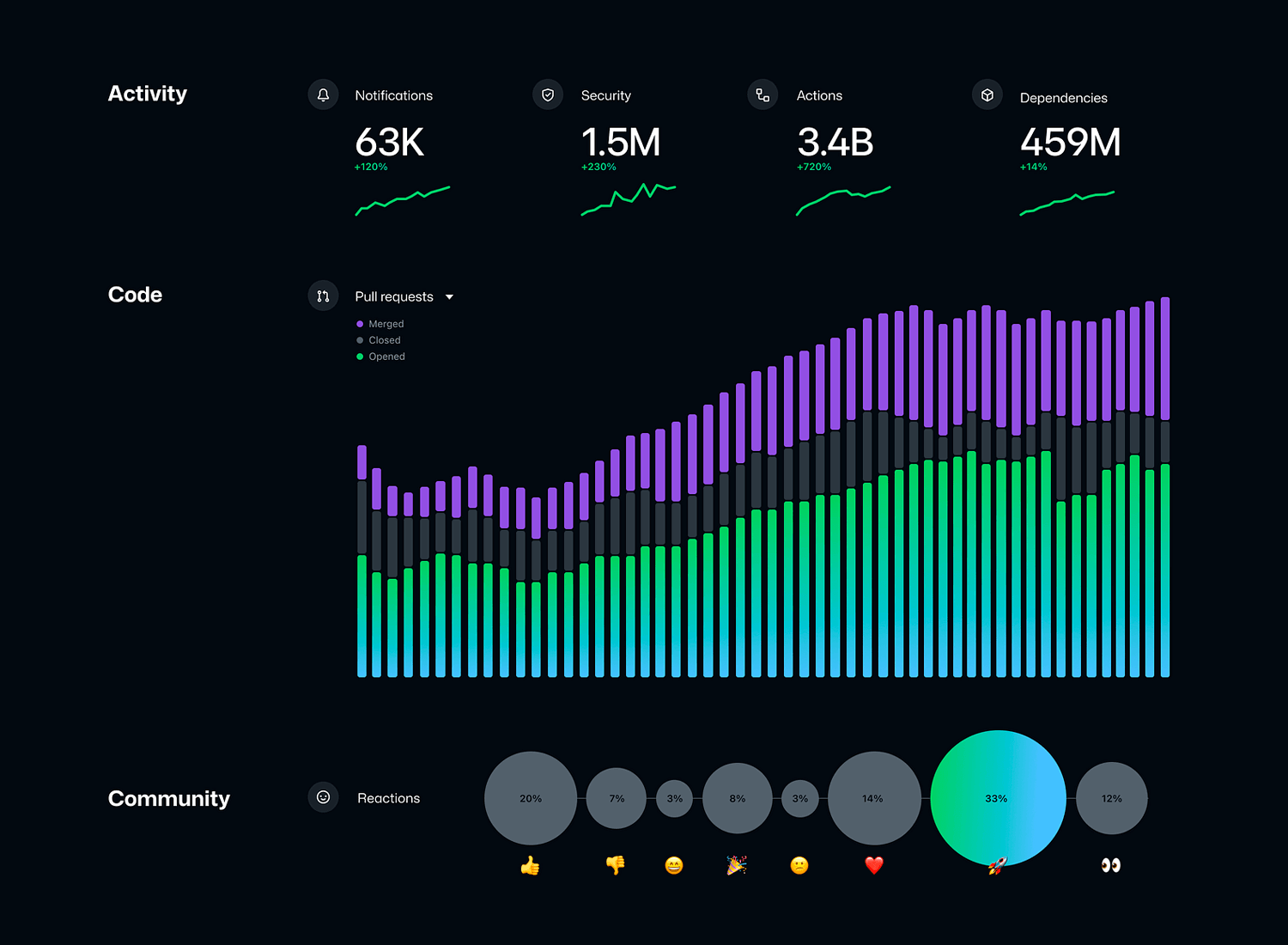
Tracking multiple metrics is easy with this type of data visualization. It uses a dark background and bright colors to show activity, code, and community reactions. The top section has line graphs for notifications and security.
A stacked bar chart shows pull requests over time, and circular charts with emojis at the bottom display community reactions. This design is visually appealing and easy to understand.
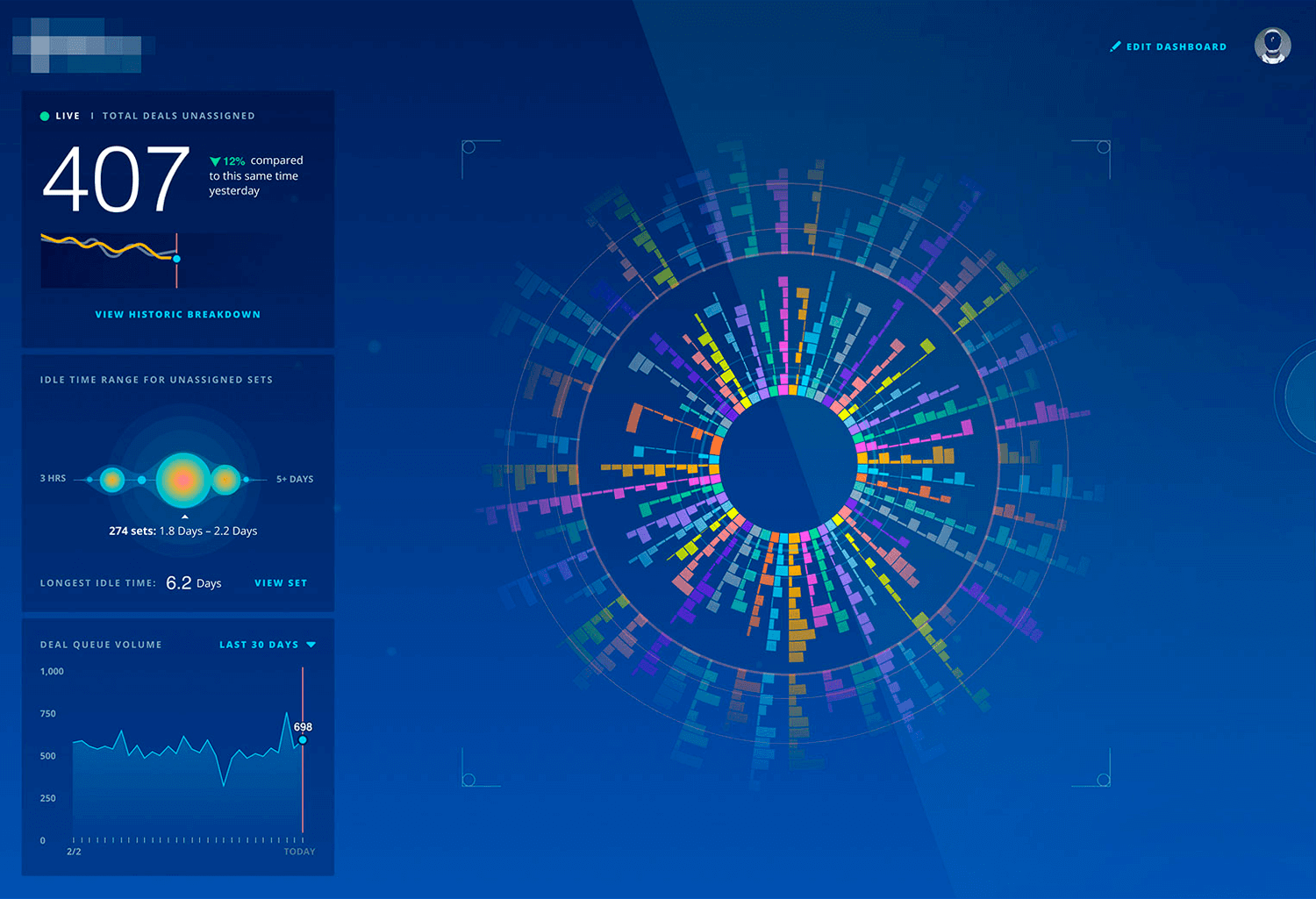
As our last example, we chose this abstract design data visualization for its unique and artistic style. The circular pattern with bright colors makes the data look both interesting and informative. On the left side, important metrics like total deals and idle times are shown with simple graphs. This design makes complex information engaging and easy to understand.
Picking the right tools to show your numbers is really important. There are lots of choices out there, some cost money, some don’t. Each one is good at different things, so think about what you need.
Tableau Public: This one is free and liked by many users. You can make great pictures with your numbers that move around, and then share them online. It’s easy to use, like building with blocks. It can do lots of different pictures, so it’s good for many things.
Google Data Studio: This one is also free and works well with other Google tools you might use. It can make pictures that move too, and you can make reports that look just how you want. It’s good if you have a team working on stuff together.
Microsoft Power BI free version: If you’re just dipping your toes into the world of data visualization, the free version of Microsoft Power BI is a fantastic place to start. Its easy drag-and-drop interface provides a user-friendly experience by letting you connect to many data sources and create dynamic dashboards.
Chart.js: If you’re a developer looking for something with a little more freedom, Chart.js might be your new best friend. This free and open-source library gives you the power to craft dynamic and responsive data visualizations that truly stand out.
Tableau Desktop: It’s the advanced version of Tableau, used by many businesses to better understand their data. It lets you make detailed charts and graphs, even with very large amounts of information. It has lots of tools to help you find patterns and make smart choices. If you need more than the free version of Tableau, this is a good upgrade.
Microsoft Power Bi Pro: This is the paid subscription of Power Bi that gives businesses more powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing data, like collaboration, sharing, and increased data capacity.

Domo: It is a business intelligence tool that lets you connect to different data sources, see real-time insights, and create custom interactive dashboards for your specific needs. It’s great for visualizing data to make informed business decisions.
Qlik Sense: This is a paid tool known for its powerful data exploration and visualization model that is easy to use for both technical and non-technical users. Its unique associative data model allows you to uncover hidden connections in your data.
Looker: It’s a Google Cloud tool, a favorite among data analysts for its ability to connect directly to databases, providing real-time analysis and customizable dashboards for powerful data visualization.
First, make sure the tool works with your existing data. Google Data Studio and Microsoft Power BI are great for this. If your team isn’t tech-savvy, choose an easy-to-use tool like Tableau Public or Google Data Studio. For more customization, Chart.js is a good option. Consider your budget, as free tools like Google Data Studio and Tableau Public are excellent, but paid options like Domo or Microsoft Power BI Pro might be worth it for extra features. For collaboration, tools like Google Data Studio or Microsoft Power BI Pro are ideal.
Creating data visualizations involves not just designing visuals but also making sure they work well in real-world scenarios. Justinmind is a great prototyping tool for this because it makes prototyping easy and dynamic.
With Justinmind, data visualization design and prototypes look and act like real applications. This helps you test and improve your designs before they are fully developed. The tool supports interactive data visualization, meaning you can add realistic data interactions. This helps stakeholders understand the final product better and gives a more accurate user experience.
One of Justinmind’s best features is Data Masters. Data Masters make your prototypes come to life with live, editable data. Unlike other tools that use static data, Data Masters let you easily add, edit, or remove data in your prototypes, making them more dynamic and realistic.
Imagine you’re creating a prototype for an application to manage clients in your company. Since your company has many clients, you’ll need some way to display them in bulk, possibly in the form of cards or tables. You’ll also need a way to edit or delete individual clients from the list and have those changes maintained across different screens in your prototype.
While a regular text table might work, it’s not very dynamic, and it’s hard to maintain if your data changes over time. How would you prototype this? With Data Masters, you can easily manage and update client data, making your prototype more functional and realistic.
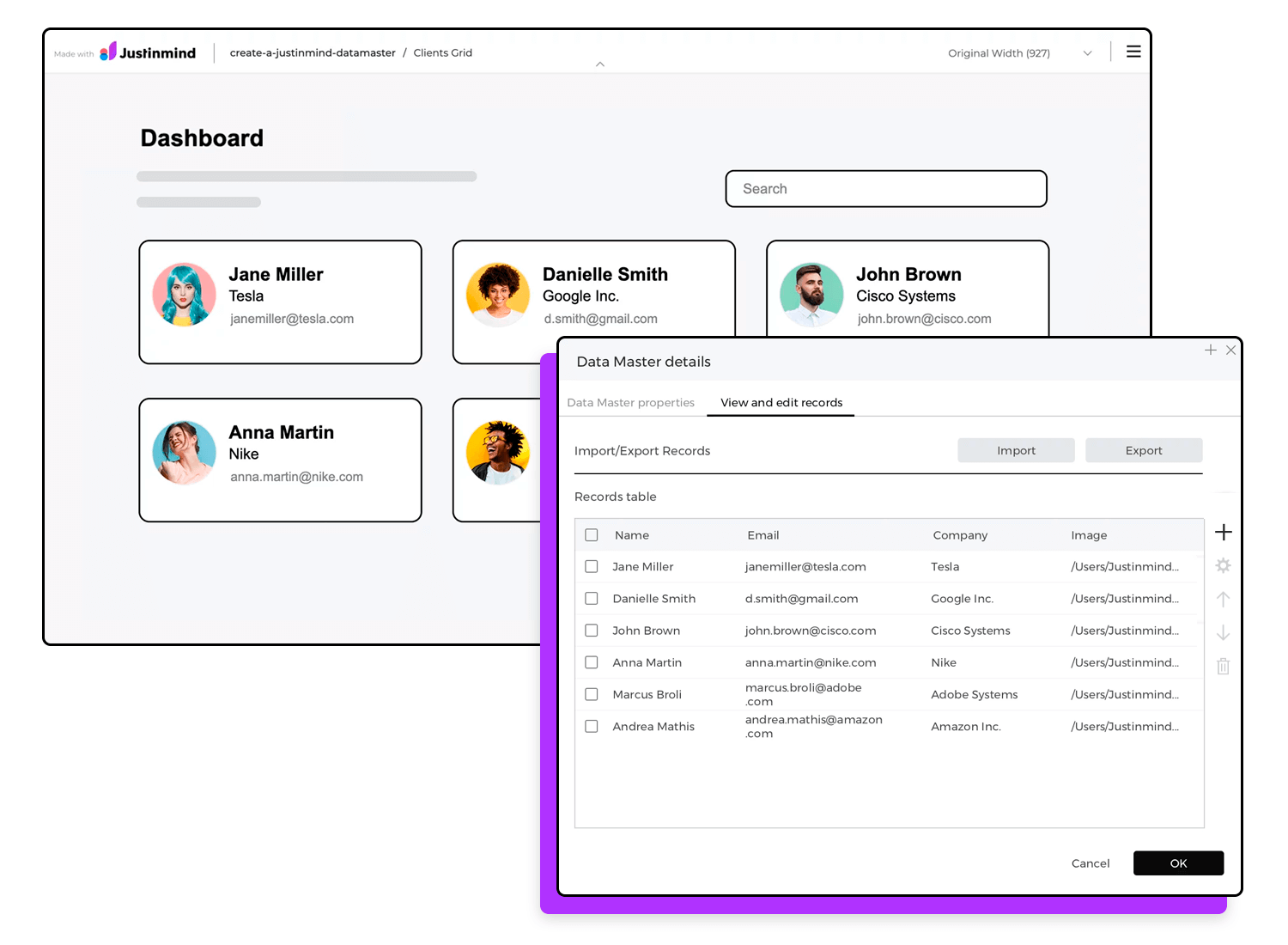
For example, you can use Data Masters to create data grids and lists that update dynamically. This is very useful for prototyping data dashboards where users need to see real-time data updates. Live data makes it easier to test different scenarios and get feedback, leading to a better final product.
If you need to show lots of information in your design, Justinmind’s data grids and lists are here to help. Data grids are like tables, perfect for organizing numbers and facts, while lists are great for displaying items in a row or column.
The best part is you can easily adjust them to fit right into your project, making your prototypes look polished and professional.
Bring your data to life with Justinmind's free prototyping tool.

Effective data visualization isn’t just about presenting data, it’s about telling a story with that data. You can captivate your audience and make your message crystal clear by mixing visuals and words, while making sure your story unfolds in a logical and compelling sequence.
Using storytelling techniques helps make data more relatable. Think of your data visualization as a story with a beginning, middle, and end. Start with an introduction to set the context and explain the purpose. For example, if you’re presenting sales data, begin by explaining why tracking sales trends is important.
In the middle, highlight key data points and trends using visual elements like charts and graphs. For example, a line graph can show sales trends over time, and a bar chart can compare sales across regions. Finally, summarize the insights and make recommendations for next steps such as strategies to boost sales in lower-performing areas.
Finding the right balance between visuals and words is key when visualizing data. While pictures like charts and graphs can quickly get across complex info, words give it meaning and context. For instance, after showing a pie chart about market share, it’s helpful to briefly explain what the numbers mean and why they matter.
Making your data visualization interactive takes it to the next level. A good example is a dashboard where you can hover over a data point to see more details. This makes the data easier to understand and gets people more interested in exploring it.

Keep your text concise, focusing on the main points. Use clear headings and bullet points to guide viewers through the story of your data so they can quickly get the main ideas without getting lost in the details.
Lay out your data in a way that makes sense for the story you’re telling. Start with the big picture, then zoom in on the details, and finish with a summary. For example, begin by showing overall sales patterns, then break it down by region, and end with how each product did.
Interactive tools like dashboards can help with this flow. They let users explore the data at their own pace, making it easier to understand complex sets of information. Use visual clues like arrows or numbers to show the order of viewing.
Make sure each part of your visualization smoothly leads into the next. This creates a story that’s easy to follow. For example, you could use linked charts that show overall sales, then regional sales, and then product-specific details.
Data visualization is about turning complex data into clear, engaging stories. Using tools like the ones we mentioned, you can create visuals that highlight trends, reveal patterns, and support smart decisions.
Key principles include knowing your audience, telling a clear story, choosing the right charts, keeping designs simple, using colors wisely, providing context, and ensuring accuracy. Clean and organize your data before visualizing it.
Good examples of visualization show how design can make data easy to understand. Tools like Justinmind help bring these designs to life with interactive, real-time prototypes. Mixing visuals with storytelling makes your data more compelling and easier to grasp. Effective data visualization blends art and science, turning raw data into insights that inform and inspire.